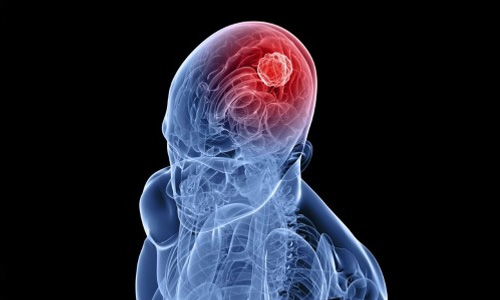
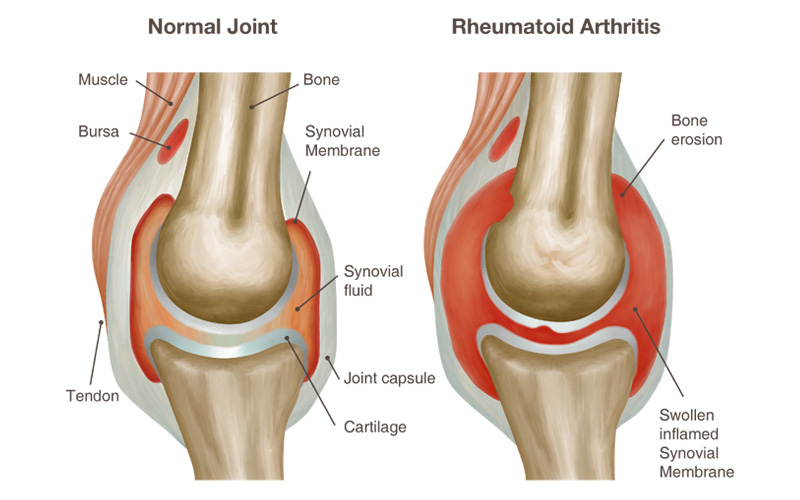
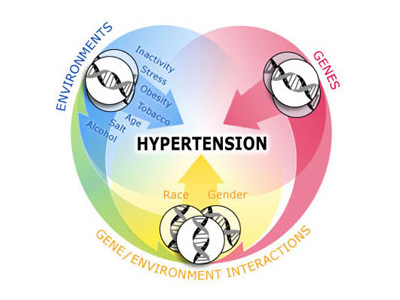
Stroke occupies one of the leading positions among diseases representing a mortal danger to humans. The problem is that in early stages it is quite difficult to recognize this disease. A little numbness in the arm, dizziness, being tongue-tied – few people will attach importance to these symptoms. Neither the patient nor his family can even […]